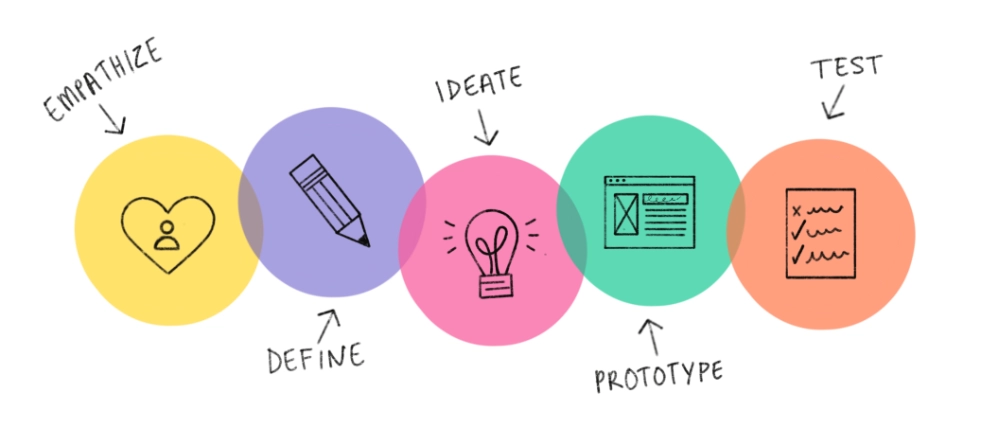
Design thinking is, above all, a highly specific mindset encompassing a wide range of practices and methods used by designers. The approach, which ties up together all these actions within a common methodology, has managed to make its way into the corporate world and win a seat at the table next to other, more linear, processes.
For this article, we will follow the 5 iconic steps from Standford d.school: empathise, define, ideate, prototype and test. To accompany you in your venture, we selected several template workshops out of our template library. Enjoy!
1. Empathize
Empathize is the stage where you try to understand the problem from the perspective of the end-user. It involves observation, interaction, and conversation with users to gain insights into their experiences, behaviors, and motivations. The goal is to gain empathy and a deep understanding of the users’ needs and challenges.

Validate assumptions about users’ unmet needs
This technique will enable us to validate assumptions of what might be the unmet needs of our targeted users.
We will do that in 3 consecutive phases:
- List the needs and identify the key questions for the interview (Step 1 to 6)
- Interview the users (Step 7)
- Reformulate the needs (Step 8)
Know Wonder about data & insight
KnoWonder is a simple yet powerful tool that will enables us to quickly capture what we know about our topic what we are still wondering about it.
Customer empathy map
The Customer Empathy Map is a tool used to increase your Understanding of your customer. By putting yourself in his own shoes, you will be able to truly understand the client's buying behaviour. Ultimately, it is often used to improve the customer experience.
In this collaborative session, we will:
- Identify your customer behavior
- Find the pains and gains of your customer
- Discuss about it with an insight cloud
- Think about solutions for your customer
- Select the best solution and discuss it
Use our library of templates to build workshops!
Stormz is an easy-to-use facilitation platform for productive ideation sessions: onboard participants in 30 seconds, nobody is left behind, everybody is enjoying the ride!
2. Define
This stage involves synthesizing the insights gathered during the empathize stage and defining the problem in a way that can guide the solution-finding process. It’s important to make sure that the problem definition is based on the users’ needs and is not just a reflection of what is technically feasible or what the organization wants to achieve. Maybe the collection of insights made you realise that the actual challenge is not what was previously announced?
These three workshops will prove critical in helping you understand what users expect, before moving on to the ideation phase:
Define your goals & challenges
The purpose of this workshop is to identify your primary goals, wishes and challenges during the course of the creative process:
- The initial divergent phase consists in a silent brainstorming sequence followed by a traditional one.
- The convergent phase will, using the $100 budget game followed by the 3 “I”’s technique, select the one wish you will keep for the second step.
Formulate challenges
Its purpose is to sharpen awareness of the challenge and create challenge questions that invite solutions.
In this workshop, the team will go through:
- A divergent phase to generate as many challenge statements as possible. To do so, they will use the Word Dance technique.
- A convergent phase to select the one challenge
3. Ideate
The Ideation phase focuses on a wide range of potential solutions to the problem (divergence) and selecting the best ones to solve your challenge (convergence). Divergence is meant to encourage creativity and out-of-the-box thinking whereas convergence lets you integrate notions of feasibility or viability. Each of the following brainstorming templates integrates a phase of convergence to select the best ideas but in case you feel like this will not be enough, we added an extra convergence workshop:
Brainstorming - Brainwriting 6-3-5
It’s a highly dynamic and creative brainstorming session (usually done in silence) that generates an extremely large number of ideas. After having submited 3 ideas in the bucket assigned to them, every participant gets a new bucket and, on the basis of the 3 ideas generated in the first step, adds 3 more. And so on... until the voting phase to select the best ideas.
Brainstorming – Find wild ideas
This is a simple 5-step collaborative workshop that enables participants to generate, select and enrich ideas capable of solving your business problems and challenges in the most creative way and then select the best ones.
Generate ideas
Its purpose is to generate ideas that answer the challenge questions.
This activity is made of 2 phases:
- A divergent phase to generate as many ideas as possible. To do so, the team will use 3 different techniques: brainstorming, Super-Powers and Forced Connections.
- A convergent phase to select the one idea that will be taken over to CPS - 5. Develop Solutions. To do so the team will use a simplified version of the COCD Idea Box.

COCD Box – Select wild ideas
Selecting ideas after a divergent phase can be jeopardized by self-censorship. This workshop will enable you to sort your ideas in three categories : common and feasible (NOW), original and feasible (WOW) or original and not (yet) feasible (HOW).
4. Prototype
In this stage, you take the most promising ideas and create rough, quickly-made models that allow you to test and experiment with your solution. The goal is to create something tangible and real that can be tested and refined. Prototyping allows you to quickly test and validate your ideas and make changes as necessary.
Your idea may not need a physical prototype, so here are different possibilities of workshops:

Prototyping – Make ideas or strategies tangible
A most critical part of Design Thinking, prototyping makes the connection between the ideation and implementation phases in many iterations. This sequence is made out of 3 steps : ideation, prototyping, collective iterations.
Identify who will assist or resist you
This workshop’s purpose is to identify the people or organizations who may have a say in the success, or failure, of your entreprise. You will therefore learn how to involve them more or, alternatively, how to neutralize them.
Building an action plan
Build an action plan to implement your idea.
5. Test
This is the stage where you get feedback on your solution from users and other stakeholders. Testing allows you to see how your solution performs in the real world and identify areas for improvement. This stage is critical in refining the solution and ensuring that it meets the needs of the end-users.
Retrospective – Learn from the past
Once your project is finalized, it is important to take a step back and gather all the relevant feedback. This sequence will help you think about what you’ve learnt, share it with the other participants and reflect on the mistakes you’ve made or obstacles you’ve encountered.
There you have it : 12 workshop templates you can freely use for Design Thinking. Other workshops are also available in the template library. If you think of any other tools or technique you’ve been using, we would be happy to talk about it with you and add them to our selection.